Protein Crops: Advancing in Agronomy to Benefit from Varietal Progress
Protein Crops: What Progress Can Be Observed Thanks to Variety Selection and Genetics?
Avoidance Strategy
Advancements in the breeding of new varieties of protein crops have led to real progress. Although they do not provide direct resistance to fungal diseases, they open the door to effective avoidance strategies. Nevertheless, rigorous management of sowing remains crucial.
Climate Change
The implications of climate change on the diseases of legume crops remain complex to predict.
Particularly for pathogens dependent on free water or high relative humidity. This uncertainty is exacerbated by the imperfect representation of precipitation and atmospheric or soil moisture in current climate models.
Varietal innovation thus constitutes a crucial pillar of hope.


Resistance to Diseases
Selection and genetic advancements have significantly contributed to the improvement of protein crops. However, resistance to fungal diseases or pests is not always immediately evident in the varieties obtained. There are many false messages claiming that protein crops are tolerant to bacterial blight or ascochyta. Indeed, there are far too many strains of bacterial blight to find radical solutions.
Moreover, the selection of protein crops faces a fundamental parameter: the presence of the disease in experimental plots. As this is not always the case, these developments take a long time to achieve. However, notable progress has been made in terms of disease resistance in current varieties, illustrated by:
- Bacterial blight, circumvented by avoidance strategies such as delaying vegetative recovery and intensive branching.
- Ascochyta and cholétrytic, also evaded thanks to vigorous recovery after winter and a higher initial pod height.
Selection Criteria for Pulse Crops
Today, the main selection criteria for pulse crops focus on:
- yield,
- disease resistance,
- lodging resistance,
- harvest height,
- seed quality to facilitate marketability.
With resistance to very cold temperatures (down to -15°C), the cold resistance of pulse crops is currently at its maximum. They also have improved lodging resistance, with results sometimes doubling over 20 years. The goal is to maintain this level.
At Agri-Obtentions, we therefore prioritize these 5 main criteria.
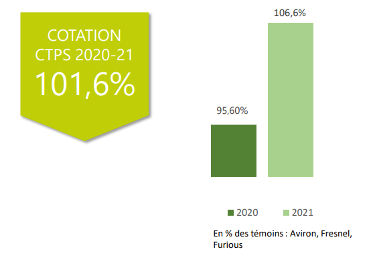

Effectiveness of Protein Crop Varieties
At Agri Obtentions, the recent fava bean varieties show yields at 118% compared to the controls. They also maintain cold resilience comparable to that of the best current varieties, such as Diva. This advancement is not always immediately noticeable to farmers.
To see the difference, it would be interesting for them to conduct a direct comparison by simultaneously growing both old and recent varieties. In parallel, new spring pea varieties resistant to aphanomyces are in the approval phase.
These can demonstrate significant tolerance with scores of 6 to 7 out of 9, far surpassing the control lines, which at best reach a score of 3. It is important to note that the cultivation of fava beans does not encourage the proliferation of the pathogenic fungus in question.
Effectiveness of Protein Crop Varieties
At Agri Obtentions, the recent fava bean varieties show yields at 118% compared to the controls. They also maintain cold resilience comparable to that of the best current varieties, such as Diva. This advancement is not always immediately noticeable to farmers.
To see the difference, it would be interesting for them to conduct a direct comparison by simultaneously growing both old and recent varieties. In parallel, new spring pea varieties resistant to aphanomyces are in the approval phase.
These can demonstrate significant tolerance with scores of 6 to 7 out of 9, far surpassing the control lines, which at best reach a score of 3. It is important to note that the cultivation of fava beans does not encourage the proliferation of the pathogenic fungus in question.
